3D-Printed Chitosan: From Material Breakthroughs to the Clinical Future of Personalized Dressings
Rapid hemostasis and wound dressings capable of adapting to irregular wound surfaces are crucial for treating infected wounds. In recent years, customizable 3D-printed hydrogels have attracted significant interest due to their ability to match wound morphology, load therapeutic agents, and deliver precise treatment. However, many existing hydrogels still suffer from limitations such as low mechanical strength and insufficient bioactivity, restricting their use in high-demand wound management.
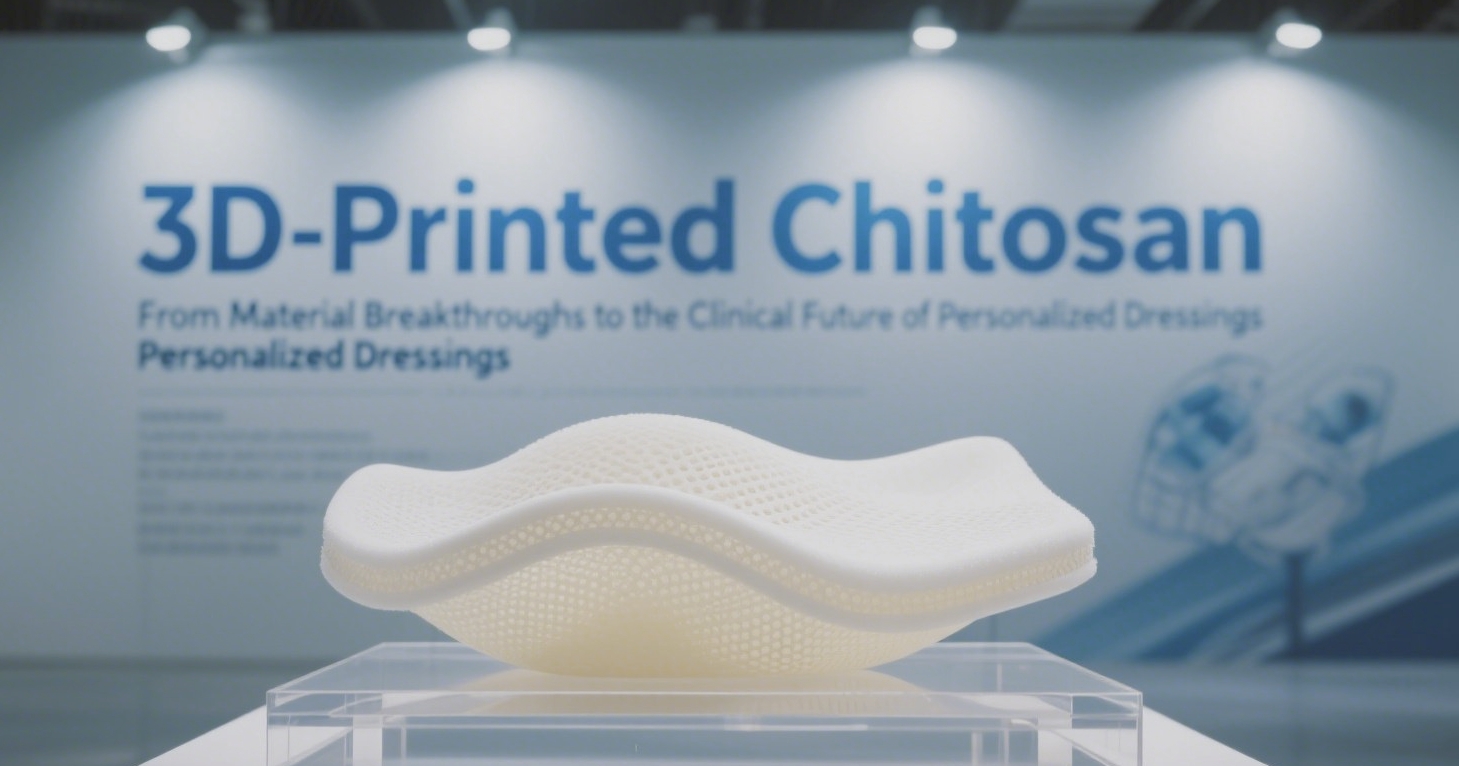
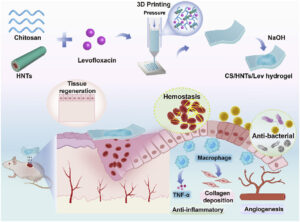
Recently, a team from Jinan University published a research article titled “3D printing of chitosan hydrogel reinforced with tubular nanoclay for hemostasis and infected wound healing” in Bioactive Materials, offering new insights into these challenges. The team developed a significantly enhanced 3D-printing hydrogel system by combining chitosan (CS) with halloysite nanotubes (HNTs).
Scientific Background: A Key Breakthrough at the Material Level
The study highlights that hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions between HNTs and chitosan endow the CS/HNTs ink with rheological properties well-suited for 3D printing, including:
-
Shear-thinning behavior
-
High printing precision
-
Excellent shape fidelity
These characteristics ensure that the material can be smoothly extruded during printing and rapidly stabilize afterward, allowing it to conform to complex and irregular wound geometries.
Furthermore, the addition of HNTs significantly improves the compressive and tensile strength of the chitosan hydrogel. As a result, the printed material can not only cover wounds but also maintain structural integrity under dynamic conditions.
The researchers also incorporated levofloxacin, an antibacterial agent, into the hydrogel to enable sustained drug release, helping reduce infection, control inflammation, and promote tissue repair.
In vitro studies demonstrated that the CS/HNTs/Lev hydrogel exhibits strong antibacterial activity, efficient coagulation, good hemocompatibility, and excellent cytocompatibility. In infected mouse models, the composite material achieved rapid hemostasis, effective antibacterial performance, and notably accelerated wound healing.
These findings show that nanoclay-reinforced 3D-printed chitosan hydrogels not only perform exceptionally well in laboratory tests but also hold strong potential for future clinical translation.
From Research to Industry Trends: The Future of Personalized 3D-Printed Dressings
The material framework presented in this study further advances the feasibility of applying 3D printing to wound care. Its printability and structural stability make several application scenarios increasingly realistic:
-
Designing patient-specific dressings based on wound geometry
-
Point-of-care rapid printing at hospitals, emergency centers, or field environments
-
Integrating antimicrobial drugs, bioactive agents, or sensors for multifunctional therapy and monitoring
-
Transforming dressings from simple coverings into functional tissue-engineering platforms
Personalized dressings are becoming a key direction in advanced wound care. Within this trend, chitosan stands out as one of the most promising base materials thanks to its natural antibacterial properties, biodegradability, and cell-friendly characteristics.
Market Outlook: Chitosan Materials Will Experience Rapid Growth in the Next 5–10 Years
Globally, the demand for chronic wound treatment—including diabetic foot ulcers, burns, and pressure ulcers—continues to rise. Industry reports estimate that the chronic wound care market alone has already reached tens of billions of dollars. With aging populations expanding worldwide, the need for high-performance dressings will continue to grow.
Chitosan composite materials offer several benefits for industrialization:
-
Abundant and sustainable raw materials
-
Natural antibacterial activity without reliance on antibiotics
-
Low allergenicity and high safety
-
Scalable production compatible with industry standards
-
Suitable for both marine-sourced and vegan-sourced supply chains
Combining scientific advancements with market demand, chitosan composites are expected to become one of the fastest-growing material systems in the medical dressing field over the next 5–10 years, especially in premium applications such as smart dressings, antimicrobial dressings, and personalized wound repair.
Conclusion
From fundamental material optimization to improved printability and enhanced antibacterial and healing performance, chitosan-based composite hydrogels are driving wound care from standardized approaches toward personalized and functional solutions. As research progresses and technologies mature, these materials are poised to become core components of next-generation clinical dressings, offering more efficient, precise, and patient-centered wound management.
Hainan Sincere Industries Co., Ltd. provides chitosan and a full range of chitosan-based products. Inquiries are welcome.







