2 Dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE) : Multifunctional Intermediate for Industrial & Pharmaceutical Innovation
Overview
2 Dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE), also known as dimethylethanolamine, is a versatile organic compound with a unique dual-functional structure combining an alcohol group and a tertiary amine. This colorless to pale yellow liquid, characterized by a faint ammonia-like odor, is highly soluble in water and organic solvents. Synthesized through the reaction of ethylene oxide with dimethylamine, DMAE serves as a critical intermediate in chemical manufacturing. Its reactivity and ability to act as a pH adjuster, catalyst, or surfactant make it indispensable in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to coatings.
Key Industrial Applications Of DMAE
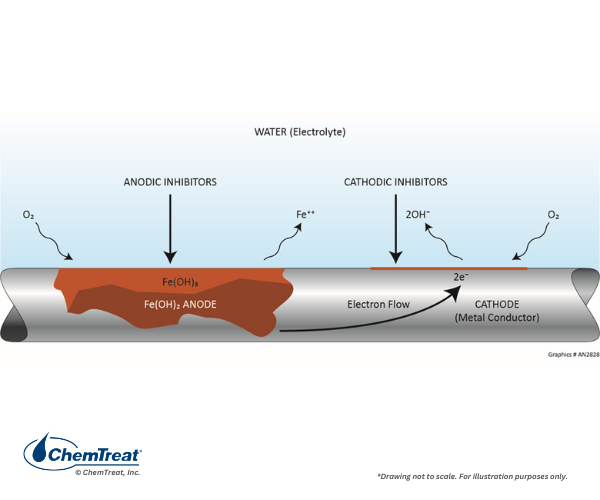
DMAE’s multifunctional properties drive its use across diverse sectors:As a key component in corrosion inhibitors, it neutralizes acidic contaminants and protects metal surfaces in industrial cooling systems. It is utilized in synthesizing anticholinergic drugs and local anesthetics, while its cholinergic properties support neurological research.In cosmetics, DMAE stabilizes formulations, enhances skin firmness, and acts as an antioxidant in anti-aging products. DMAE accelerates epoxy resin curing and improves adhesion in paints, ensuring durable finishes.As a dye-fixing agent, it enhances color fastness and reduces wastewater toxicity.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
2 Dimethylaminoethano (DMAE )is biodegradable under aerobic conditions, but its environmental impact requires careful management. High concentrations in aquatic systems can be toxic to microorganisms, necessitating controlled wastewater treatment to meet regulatory standards. In industrial settings, vapor emissions should be minimized using closed systems or scrubbers to prevent air quality issues.
From a safety perspective, it poses moderate risks. Direct contact with skin or eyes may cause irritation, and prolonged exposure to vapors can lead to respiratory discomfort. Proper PPE—gloves, goggles, and respirators—is essential during handling. Storage in cool, well-ventilated areas away from oxidizers and acids prevents hazardous reactions.
Conclusion
2 Dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE) exemplifies the synergy of functionality and adaptability in industrial chemistry. Its role in enhancing product performance—from durable coatings to advanced pharmaceuticals—underscores its irreplaceable value. As industries prioritize sustainability, innovations in DMAE recycling and greener synthesis methods will further solidify its position as a responsible choice for modern manufacturing. With ongoing research into novel applications, DMAE continues to pave the way for efficient, high-performance solutions across global markets.