One Of The Most Comprehensive Introductions on Chitosan In History-The Origin, Basic Properties And Applications
Chitosan
The product obtained by deacetylation of chitin in nature
Chitosan, also known as deacetylated chitin, is obtained by deacetylation of chitin, which is widely present in nature. Its chemical name is β-1,4-poly-glucosamine[1]
Since 1859, when Frenchman Rouget first obtained chitosan, the excellent properties of this natural polymer, such as biofunctionality, compatibility, blood compatibility, safety, and microbial degradability, have attracted wide attention from all walks of life, and significant progress has been made in the application research in many fields such as medicine, food, chemical industry, cosmetics, water treatment, metal extraction and recovery, biochemistry and biomedical engineering. For patients, there are research reports on the effect of chitosan in lowering blood lipids and blood sugar. At the same time, chitosan is included in the national food additive use standard GB-2760 as a thickener and filming agent.
Basic information
- Name:Chitosan
- Chemical name:Polyglucosamine (1-4)-2-amino-B-D
- Application:Medicine, food, chemical industry, cosmetics
- Discoverer:Rouget
- Alias:Deacetyl chitosan
Material structure
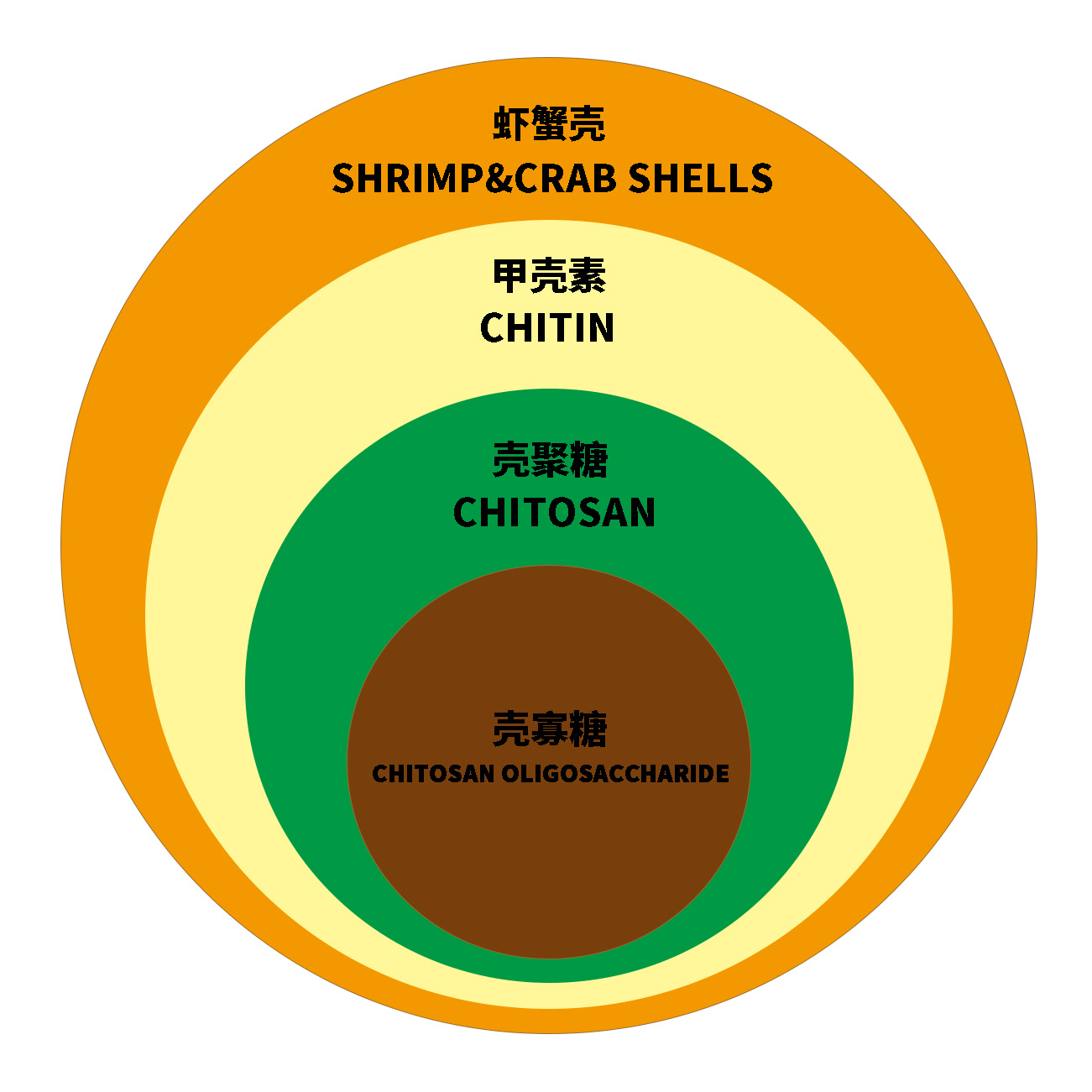
Relationship with chitin

Chitosan is the product of chitin deacetylation. Generally speaking, chitosan is defined as the product with more than 55% of N-acetyl removed. In other words, chitosan is defined as the product that can dissolve 1% of deacetylated chitosan in 1% acetic acid or 1% hydrochloric acid. In fact, chitosan with an N-deacetylation degree of more than 55% can be dissolved in such dilute acid. As an industrial product, chitosan has an N-deacetylation degree of more than 70%. Chitosan with an N-deacetylation degree of 55% to 70% is low-deacetylation chitosan, chitosan with a N-deacetylation degree of 70% to 85% is medium-deacetylation chitosan, chitosan with a N-deacetylation degree of 85% to 95% is high-deacetylation chitosan, and chitosan with a super-high-deacetylation degree of 95% to 100% is super-high-deacetylation chitosan. Chitosan with an N-deacetylation degree of 100% is extremely difficult to prepare. There may or may not be N-acetyl groups on each sugar group of chitin. Any chitin with an N-acetyl degree below 50% is called chitin because it is definitely insoluble in the above-mentioned dilute acid concentration.
Degree of deacetylation
The degree of deacetylation (D.D) determines the amount of amine groups (NH2) on the macromolecular chain. As D.D increases, the number of charged groups on chitosan in dilute acid solution increases due to protonation of the amine groups, and the charge density of the polyelectrolyte increases, which will inevitably lead to changes in its structure, properties and performance. So far, studies on the properties of dilute chitosan solutions have ignored the effect of D.D value on the equation. VANDUM et al. studied the effect of different ionic strengths on the molecular size and viscosity of chitosan in dilute solutions. The results showed that different ionic strengths would change the expansion of random coils and thus change the molecular size and intrinsic viscosity. By measuring the MARK-HOUWINK equation constants for chitosan with different D.D values, the results showed that the K, A values change with the D.D value. Therefore, the constants K and A of the MARK-HOUWINK equation change regularly depending on the deacetylation degree of chitosan, and at the same molecular weight, as the deacetylation degree increases, the molecular size, intrinsic viscosity and expansion factor of chitosan in dilute solution increase, while the characteristic ratio and steric hindrance factor decrease with the increase of deacetylation degree. Therefore, the average molecular weight of any chitosan sample within the applicable range can be calculated by a relatively simple intrinsic viscosity measurement.
Physical and chemical properties
Physical properties
Pure chitin and pure chitosan are both white or off-white translucent flaky or powdery solids, tasteless, odorless, non-toxic, and pure chitosan has a slight pearly luster. The relative molecular mass of chitin in organisms is 1×106~2×106. The relative molecular mass of chitin after extraction is about 3×105~7×105. The relative molecular mass of chitosan made from chitin is even lower, about 2×105~5×105. In the manufacturing process, the relative molecular mass of chitin and chitosan is generally expressed by the viscosity value. Commercial chitosan has three different viscosities depending on its use, namely, high viscosity products are 0.7~1Pa·s, medium viscosity products are 0.25~0.65 Pa·s, and low viscosity products are <0.25 Pa·s. High-viscosity chitin or chitosan must be used to manufacture fiber products.

Chemical properties
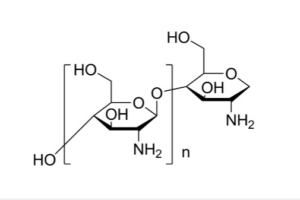
Chemical name: β-(1→4)-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose
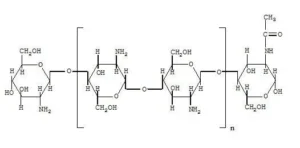
Molecular formula: (C6H11NO4)N
The molecular weight of the unit is: 161.2
The structural formula is shown in the figure
Under certain conditions, chitosan can undergo chemical reactions such as hydrolysis, alkylation, acylation, carboxymethylation, sulfonation, nitration, halogenation, oxidation, reduction, condensation and complexation, and can produce various chitosan derivatives with different properties, thereby expanding the application range of chitosan.
There are active hydroxyl and amino groups in chitosan macromolecules, which have strong chemical reaction ability. Under alkaline conditions, the hydroxyl group on C-6 can undergo the following reactions: Hydroxyethylation – chitosan reacts with ethylene oxide to obtain hydroxyethylated derivatives. Carboxymethylation – chitosan reacts with chloroacetic acid to obtain carboxymethylated derivatives. Sulfonation – chitin and chitosan, like cellulose, can react with carbon disulfide to form sulfonates after being treated with alkali. Cyanoethylation – acrylonitrile and chitosan can undergo addition reaction to produce cyanoethylated derivatives.
The above reaction introduces large side groups into chitin and chitosan, destroying their crystalline structure, thereby improving their solubility and making them soluble in water. The carboxymethylated derivatives show the properties of polyelectrolytes in solution.
Application fields
1. Chitosan for cosmetics
Chitosan for cosmetics has good moisture absorption, moisturizing, conditioning, antibacterial and other functions; it is suitable for moisturizers, shower gels, facial cleansers, mousses, high-end creams, lotions, colloid cosmetics, etc.; it effectively makes up for the defects of general chitosan.
2. Chitosan for flocculants
Chitosan and its derivatives have good flocculation and clarification effects. As a clarifier for beverages, it can quickly flocculate suspended matter and precipitate naturally, thereby increasing the yield of the stock solution; in Chinese medicine extracts, large molecular proteins, tannic acid and pectin can be easily removed with chitosan solution, and the effective ingredients of Chinese medicine with higher purity can be refined; the adsorption of chitosan has a good effect on water purification.
3. Chitosan for agriculture, feed and bait
Chitosan is a natural plant nutritional growth promoter – the raw material of foliar fertilizer. The foliar fertilizer compounded with chitosan can not only kill insects and resist diseases, but also act as a fertilizer. Decompose animal and plant residues and trace metal elements in the soil, thereby converting them into nutrients for plants, enhancing plant immunity and promoting plant health; shrimp shells and crab shells are rich in protein and trace elements. After animals eat and absorb them, there are Good nutritional value.
4. UTA (adsorbent) special chitosan
UTA’s special chitosan is a series of chitosan products processed through a special process; it can effectively adsorb protein, 40% higher than the adsorption of general chitosan.
5. Chitosan special for tobacco (tobacco gum)
This product can be evenly mixed with shredded tobacco and can adhere to the surface of shredded tobacco. It can enhance tensile strength, water resistance, and bursting resistance. It is not easily broken during processing and is suitable for modern high-speed cigarette making machines. This tobacco additive can make cigarettes burn better. The performance is significantly enhanced, and it has the effect of reducing tobacco tar and nicotine content, reducing the cigarette smoke, reducing harmful substances in the smoke, improving the smoking taste, and revealing the aroma; it can also effectively inhibit tobacco leaf mildew and prolong the life of tobacco. Save time.
Cosmetics
1. The origin of chitosan in cosmetics
Since 1859, when Frenchman Rouget first obtained chitosan, the French began a long research on further purification of chitin.
2. The role of chitosan in cosmetics
Until 1997, the Biomedical Department of the University of Brittany in the South, the most beautiful university in the world, specialized in marine biology, used low-temperature inert gas extraction technology to extract high-purity and high-activity chitosan from shrimps to purify chitosan with up to 95% deacetylation. Only chitosan with a content of 95% deacetylation is more active in medicine, more skin-friendly, and has a targeted effect on wound healing and antibacterial and antiviral.
Due to the influence of radiation in the Japanese waters, more than 70% of the best medicinal chitosan currently comes from the Brittany region of France.
Chitosan is currently used in skin care products as an ingredient used in advanced cosmeceuticals. It is used in pulsed light, radio frequency, fractional matrix, fruit acid and other medical cosmetics to play the role of natural antibiotics to resist sensitivity and inflammation, quickly repair basal thermal damage, quickly heal wounds, and repair epidermal barriers. In addition, chitosan skin care products also have the function of metabolizing heavy metals.
3. Cosmetic brands with chitosan
As of 2013, skin care products containing marine chitosan include French MedSpa, French Channel, American Estee Lauder, etc.
Food field
- Antibacterial agent
Chitosan and its derivatives have good antibacterial activity and can inhibit the growth and reproduction of some fungi, bacteria, and viruses. As of 2013, it is believed that there are three possible mechanisms: first, due to the polycation of chitosan, it is easy for the negatively charged groups on the surface of fungal cells to act, thereby changing the fluidity and permeability of the cell membrane of pathogens; second, it interferes with DNA replication and transcription; third, it blocks the metabolism of pathogens. Since 2010, many researchers have proposed that chitosan can achieve the purpose of antibacterial by inducing pathogenesis-related proteins, accumulating secondary metabolites and signal transduction.
Papineau et al. believed that due to the interaction between the positive charge of chitosan molecules and the negative charge on the bacterial cell membrane, the protease and other components in the cell leak out, thus achieving antibacterial and bactericidal effects. Their research found that chitosan lactate at a dosage of 0.12 mg/ml had a good inhibitory effect on the reproduction of Escherichia coli, and chitosan glutamate also had a good inhibitory effect on the reproduction of yeast such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and 1 mg/mL chitosan lactate would completely inactivate the yeast within 17 minutes. Sudharshan et al. pointed out that because chitosan can penetrate into the nucleus of bacteria and bind to DNA, it inhibits the synthesis of mRNA, thereby hindering the synthesis of mRNA and protein, achieving antibacterial effects. They studied the effects of water-soluble chitosan such as chitosan lactate, chitosan glutamate and chitosan hydrogenated glutamate on the cultivation of different bacteria. The results showed that chitosan lactate and chitosan glutamate had high antibacterial effects on both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Ghaoth et al. showed that strawberry corruption caused by B. Cinerea or R. Stolonifer was significantly inhibited after being coated with chitosan solution, which can extend the shelf life of strawberries. In addition, studies have reported that chitosans of different molecular weights have different preservative effects, among which chitosans of about 200,000 and 10,000 are the best. In addition, in 2013, the preservatives used in most condiments were benzoic acid and its sodium salt. Compared with them, under the same storage conditions, chitosan has a better antibacterial effect, less dosage, good taste, and no toxic side effects. It is an ideal condiment preservative. Yang Jisheng et al. studied the preservative effect of chitosan on soy sauce. The results showed that adding 0.1% chitosan to soy sauce had a significant inhibitory effect on the yeast group that caused the soy sauce to deteriorate. It can be stored for 30 days under open conditions in summer without deterioration, and does not affect the taste, color, aroma and ingredients.
2.Fruit and vegetable preservatives
The purpose of fruit and vegetable preservation is mainly to keep fruits and vegetables fresh from picking until the shelf life, so as to maintain normal quality, taste, nutritional content and appearance, and improve their commodity value. Chitosan is used for coating preservation. The film layer has permeability and water resistance, which can increase the penetration resistance of various gas molecules, forming a micro-atmosphere environment, which increases the carbon dioxide content in the fruit and vegetable tissues and reduces the oxygen content, inhibits the respiratory metabolism and water loss of fruits and vegetables, and slows down the aging of fruit and vegetable tissues and structures, thereby effectively extending the post-harvest life of fruits and vegetables. The research results of Chen Tian et al. using chitosan to preserve kiwifruit at room temperature showed that at room temperature, the storage life of kiwifruit preserved with chitosan aqueous solution can reach 70-80 days, while the control treatment is only 10-13 days. Wang Gang et al.’s research shows that when kiwifruit is coated for preservation, the molecular weight of chitosan also affects the preservation effect, among which chitosan with a viscosity of 100-300cp is better than chitosan with a viscosity of more than 1000cp.
Research results on the preservation of tomatoes by chitosan show that chitosan can significantly slow down the color change of tomatoes and can also help maintain the hardness of the fruit. The higher the concentration of chitosan, the better the preservation effect. Research on the use of chitosan for apple preservation shows that the coating can hinder the decline of vitamin C during storage, reduce the respiratory intensity of apples and reduce membrane lipid peroxidation of post-harvest apples. Lesper et al. used 2% modified chitosan to coat the surface of citrus and apples. As a result, no obvious spots appeared on the citrus after being stored at 30°C for a week, while the opposite was true for the other half. Chen Anhe’s research showed that after strawberries treated with 1% chitosan solution were stored for a period of time, the superoxide dismutase and vitamin C contents still remained at high levels.
3. Antioxidants
Meat products contain high levels of unsaturated lipid compounds that are easily oxidized, causing them to spoil, thus shortening the storage life of meat products and destroying their flavor. Darmadji and Izumimoto studied the oxidative stability of beef treated with chitosan. The results showed that the addition of 1% chitosan reduced the thiobarbituric acid in beef by 70% after storage at 4°C for 3 days. Shahidi reported that N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan (NOOC) and its lactate and pyrrolidine carboxylate were very effective in inhibiting the oxidation of cooked meat, and the flavor of cooked meat remained almost unchanged after 9 days of refrigeration. He pointed out that the inhibitory oxidation effects of NOOC and the aforementioned chitosan derivatives were 69.9%, 43.4% and 66.3% respectively at (500-3000)×10-6. This mechanism of inhibitory oxidation is related to free iron ions and chitosan in meat. When the meat is heat treated, free iron ions are released from the hemoglobin in the meat and chelate with chitosan to form a chelate, thereby inhibiting the catalytic activity of the iron ions.
4. Health food additives
Chitosans are difficult to be digested and absorbed by the human gastrointestinal tract. When people take them into the body, they can form complexes with lipid compounds such as triglycerides, fatty acids, bile acids and cholesterol that are many times their own mass. The complexes are not hydrolyzed by gastric acid and are not absorbed by the digestive system, thus hindering the body from absorbing such substances and causing them to pass through the intestines and be excreted from the body. Therefore, chitosans can reduce fat and reduce food calories, and can be used as health food additives. Agullo et al.’s research shows that chitosans not only have a very refreshing sweet taste and the functions of regulating blood pressure, eliminating fatty liver, lowering cholesterol and enhancing immunity, but also have the function of improving the water retention and moisture regulation of food, and can be used as health food additives for diabetes and obesity.
5. Clarifier for juice
Juice contains a large amount of negatively charged substances such as pectin, cellulose, tannins and polypentosaccharides, which will make the juice cloudy during storage. When the positive charge of chitosan and the above-mentioned negative charge substances are adsorbed and flocculated, the processed clarified juice is a stable thermodynamic system, so it can be stored for a long time without causing turbidity. Studies have shown that chitosan is also a good purifier for grapefruit juice. Whether the grapefruit juice is treated with pectinase or not, the clarifying effect of chitosan is very significant. Spagna et al. reported that chitosan has good affinity for polyphenol compounds such as catechin and cinnamic acid. When chitosan is added to pure wine, due to the affinity between chitosan and polyphenolic compounds, the wine changes from the initial light yellow to deep golden yellow, which greatly improves the quality of the wine. Rwan et al. added 0.1-0.15g/mL chitosan to grape juice, and the contents of citric acid, tartaric acid, L-malic acid, oxalic acid and ascorbic acid in grape juice were reduced by 56.6%, 41.2%, 38.8% and 36.8% respectively. and 6.5%, thereby reducing the total acid content in the juice by 52.6%, and the juice is better purified.
In addition, chitosan can also be used as a water clarifying agent and enzyme immobilizing agent.
Medical applications
The main medical applications are:
1. Promoting blood coagulation and wound healing
Chitosan has the effect of promoting blood coagulation and can be used as a hemostatic agent. It can also be used as a wound filler material, which has the effects of sterilization, promoting wound healing, absorbing wound exudate, and not easy to shrink due to dehydration.
2. As a sustained-release matrix for drugs
Chitosan can be degraded by lysozyme in the body to generate natural metabolites. It is non-toxic and can be completely absorbed by the body. Therefore, it has great advantages as a sustained-release agent for drugs. Japan has already sold sustained-release drugs with chitosan as the matrix.
3.For artificial tissues and organs
The complex of chitosan and calcium phosphate can be used as a substitute for bone, for bone repair and tooth filling; the composite material of chitosan derivatives and polyester can be used as artificial blood vessels. Abewidra once launched a new material for modifying burns, ulcers and skin infections-“artificial skin”. This modified material has the function of natural skin. It can not only protect the wound from bacterial infection, but also penetrate air and moisture to promote wound healing. Chitosan and chitin can be mixed to make high-strength filamentous fibers for use as surgical sutures. This surgical suture can be degraded by lysozyme in the body. After the wound is healed, it can be fully absorbed by the body without removal and will not cause allergic reactions.
4. Has immunomodulatory activity
Chitosan has a series of biological effects that activate and mediate the body’s system and improve the systemic function of phagocytes. There are receptors for bacterial polysaccharides on the surface of macrophages, and chitosan, as an analog of bacterial polysaccharides, can stimulate macrophage activation and produce the following reactions: promote its phagocytic function and enhance its synergistic effect in other immune responses, thereby achieving the body’s regulation of T cells, NK cells and B cells, and mediating the body’s cellular immune response and humoral immune response. Therefore, chitosan has an immunomodulatory effect on the body.
5. Other medical uses
Chitosan gel can be used as a carrier of dental antibiotics, with hemostasis, anti-inflammatory and wound healing functions; it can reduce the cholesterol concentration in serum and liver, and is used as a cholesterol-lowering agent. Chitosan can strengthen liver function, prevent liver hangover caused by excessive drinking, and has the effect of adsorbing and excreting heavy metals, toxins, pesticides, and chemical pigments remaining in the body. After taking chitosan, cancer patients can activate lymphocytes with immune functions in the body, enabling them to distinguish between normal cells and cancer cells and kill cancer cells. Chitosan can adjust the pH value in the body to weak alkalinity, improve the utilization rate of insulin, and help prevent and treat diabetes. In addition, it also has the function of regulating the endocrine system, normalizing insulin secretion, inhibiting blood sugar increase, and lowering blood lipids.
Environmental protection application
Chitosan has a chelating and adsorbing effect on many substances. The amino group and the hydroxyl group adjacent to the amino group in its molecules can form stable chelates with many metal ions (such as Hg2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, CA2+, Ag+, etc.), which are used to treat heavy metal wastewater, purify tap water, and separate metal ions in hydrometallurgy. Japan is the first country to use chitosan to treat wastewater, with an annual consumption of 500 tons; the US Environmental Protection Agency has also approved the use of chitosan for drinking water purification. In addition, chitosan can adsorb dyes, proteins, amino acids, nucleic acids, enzymes, halogens, etc. through complexation and ion exchange, and is used to treat dye wastewater, printing and dyeing wastewater, and food industry wastewater, thereby purifying the environment and protecting human health.
Development Status
In China, formaldehyde and acetic anhydride were used as crosslinking agents to prepare chitosan gel LCM-X (LCM1, LCM2) based on chitosan. And its properties were studied. There are few reports on the research and application of chitosan gel at home and abroad. The prepared LCM-X is neither soluble in water, dilute acid and alkali solutions, nor in general organic solvents, but LCM-X is a gel with active groups (NH2), and has excellent properties such as good mechanical strength and chemical stability and does not require special treatment, that is, it has active groups (NH2), and its parent chitin resources are abundant and low in price. It is a biopolymer with great application prospects. However, due to the lack of a suitable dispersant, LCM-X has not been able to form a granular product, and its application is limited. This needs to be further studied and resolved.
Research on hydrogels is highly valued at home and abroad. Developing new hydrogel resources is one of the main tasks. Hydrogels have excellent biocompatibility, anticoagulation, water absorption and swelling, and good optical properties. It plays an important role in the research of immobilized enzymes, cell separation, protein preparation, sustained-release drugs, contact vortex manufacturing and artificial organs. However, there are no detailed reports on the research on the properties of chitosan hydrogels in China and abroad. Only the preliminary properties of hydrogels have been explored in China. The results show that the hydrogel with methanol as the gelling medium has the strongest swelling capacity, and the cross-linking degree is inversely proportional to the RV value of chitosan hydrogel. The research on chitosan gel needs to be further developed.
Performance
Because chitosan molecules have free amino groups, they are easy to form salts in acidic solutions and have cationic properties. As the number of amino groups in chitosan molecules increases, its amino characteristics become more significant, which is exactly where its unique properties lie, thus laying the foundation for many biological and processing properties of chitosan.
Physiological activity
1. Control cholesterol
One of the biggest problems in human health is cholesterol, which causes many serious diseases. Chitosan has two mechanisms to lower cholesterol. One is to prevent the absorption of fat, and the other is to excrete cholesterol in the human blood. First, chitosan inhibits the activity of lipases that help fat absorption. Lipase breaks down fat for the body to absorb. The other is to excrete bile acid. Once bile acid is excreted, the cholesterol in the blood is used to make bile acid. These two mechanisms make chitosan a strong cholesterol scavenger. Chitosan is a natural material with strong anion adsorption capacity, suitable for lowering cholesterol without any side effects.
2. Inhibit bacterial activity
Chitosan is easily soluble in weakly acidic solvents. It is particularly worth pointing out that the dissolved solution contains amino groups (NH2+), which inhibit bacteria by combining negative electrons. The antibacterial activity of chitosan makes it widely used in the fields of medicine, textile and food.
3. Prevent and control high blood pressure
One of the most influential factors in hypertension is chloride ions (cl-). It is usually ingested through table salt. Since 2010 many people have consumed too much salt. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme) produces angiotensin II, a material that causes vasoconstriction, and its activity comes from chloride ions. High molecular chitosan acts like dietary fiber and is not absorbed in the intestines. Chitosan excretes chloride ions through the adsorption between its own chloride ions and ammonium ions. Therefore, chitosan reduces angiotensin II. It helps prevent high blood pressure, especially in those who consume excessive amounts of salt.
4. Adsorption and excretion of heavy metals
A notable property of chitosan is its adsorption capacity. Many low molecular weight materials, such as metal ions, cholesterol, triglycerides, cholic acid and organic mercury, can be adsorbed by chitosan. In particular, chitosan can not only adsorb magnesium and potassium, but also zinc, calcium, mercury and uranium. The adsorption activity of chitosan can be selectively exerted. These metal ions are harmful in high concentrations in the human body. For example, too high a concentration of copper ions (Cu2+) in the blood can lead to copper poisoning and even carcinogenic consequences. Chitosan has been shown to be an efficient chelating medium. The adsorption capacity of chitosan depends on its degree of deacetylation. The greater the degree of deacetylation, the stronger the adsorption capacity.
5. Immune effect
Chitosan has higher protein adsorption capacity; under the action of degrading enzymes (lysozyme, kitinase), chitosan is degradable; chitosan is easily processed into threads and is suitable for making into threads or sheets Medical materials; Chitosan has affinity and solubility and is suitable for the production of various derivatives; Chitosan has higher chemical activity; Chitosan has high water holding capacity; In serum, chitosan is easily degraded and absorbed; Polysaccharides have higher biodegradability; chitosan shows a selective and highly inhibitory effect on the growth of oral streptococci without affecting the growth of other beneficial bacteria.
Risk terms
R20 Harmful if inhaled.
R21 Harmful in contact with skin
R37 Irritating to respiratory system.
R38 Irritating to skin.
Safety terms
S24/25Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
Avoid contact with skin and eyes.